
Erratum to butyrate ameliorates alcoholic fatty liver disease via reducing endotoxemia and inhibiting liver gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis
Erratum to: Ann Transl Med 2021;9:873.
This article (1) titled “Butyrate ameliorates alcoholic fatty liver disease via reducing endotoxemia and inhibiting liver gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis” (doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2158), unfortunately contains an error in Figure 3. Specifically, the transmission electron microscopy images labeled as belonging to the LPS group in Figure 3I were mistakenly used in place of images from the alcohol group. This error occurred due to an oversight in the placement of the images. The correction of this information does not affect the results and conclusions of this paper. The corrected image of Figure 3 is provided below.
Figure 3 in the original article:
The correct version of Figure 3 is presented below.
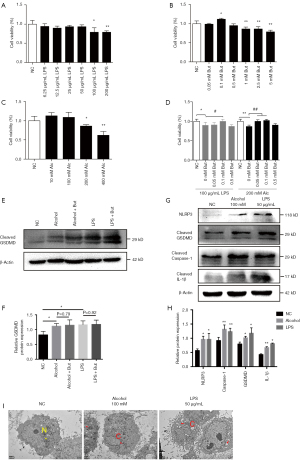
Click here to view the updated version of the article.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- Zhang T, Li J, Liu CP, et al. Butyrate ameliorates alcoholic fatty liver disease via reducing endotoxemia and inhibiting liver gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis. Ann Transl Med 2021;9:873. [Crossref] [PubMed]



