The Röttinger approach for total hip arthroplasty: technique, comparison to the direct lateral approach and review of literature
Introduction
Evidence has demonstrated that selecting the proper surgical approach is an important factor that can affect the outcome of total hip arthroplasty (THA) (1-4). Over the years, multiple approaches have been described each proposing different advantages and indications in THA (4-8). Generally, hip approaches can be broadly divided into three main categories depending on the anatomical relationship to the greater trochanter; anterior, lateral, and posterior approaches (7,9,10). Additionally, intermediate approaches in-between any two of the above have been established (10-13). Overall, posterior approaches provide wider exposure and spare the abductors muscles. However, they sacrifice the posterior capsule and potentially the external rotators and subsequently may be associated with a higher risk of dislocation (14). Conversely, the anterior and lateral approaches including the direct lateral approach described by Hardinge (9), provide adequate exposure with a reported lower risk for prosthetic dislocation (9,10,12). However, these approaches have the potential disadvantage of damaging the abductors or its nerve supply which can lead to weakness and subsequently, prolonged post-operative limping (15).
In 2004, Bertin and Röttinger (16) popularized a new minimally-invasive hip approach that utilized the plane between the tensor fascia lata and the gluteus medius muscles (16). The approach was subsequently described in different terms in multiple technical reports, including the modified antero-lateral or modified Watson-Jones approach. In this approach, the operative extremity is draped and dropped into an adducted, extended, and externally rotated position allowing for adequate femoral preparation. Moreover, it has been popularized as a minimally-invasive approach but can also be extensile in all directions while the patient is in the lateral decubitus position (17). Compared to the direct lateral approach, it offers the same advantages of this approach while avoiding iatrogenic abductor injury.
Multiple studies have reported favorable clinical outcomes with the Röttinger approach (18-20). However, others reported higher complications rate and a relatively slow learning curve (21,22). Therefore, we conducted this study to: (I) present our operative experience and technique of the Röttinger approach; (II) compare short-term complications and operative room (OR) times of this approach to the direct lateral; and (III) review the available literature for primary THA.
Methods
Patient selection
This IRB-approved study was a review of a longitudinally maintained single-surgeon database of patients who underwent primary unilateral THA using either the Röttinger or direct lateral approach (9,16). A total of 100 consecutive patients (100 hips) who underwent primary THA using the Röttinger approach (16) between April 1st, 2012 and April 30th, 2015 were identified. This cohort was compared to another cohort of 147 consecutive patients (147 hips) who underwent the procedure using the direct lateral approach (of Hardinge) (9) by the same surgeon.
Operative technique for the Röttinger approach
The patient is positioned in lateral decubitus position on a split table with the operative side up. The patient should be positioned slightly anteriorly on the operating table so that the contralateral leg lies over the anterior leg piece of the lower part of the table. The poster leg piece is then removed creating a space behind the patient for the operative leg to be dropped into during the surgery. This allows adduction, extension, and external rotation of the femur to give the surgeon access for reaming and inserting the femoral stem. The patient and the contralateral leg are securely fastened to the operating table using a variety of straps and clamps after padding all the pressure points. The operating surgeon stands anterior to the patient while two assistants stand behind the patient. One assistant will be primarily responsible for leg manipulations, while the second will aid in retraction (Figure 1).
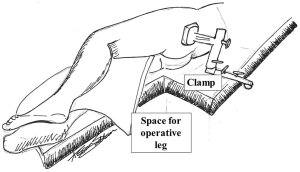
With the patient in a strictly lateral position, an anterior incision connecting the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior superior tip of the greater trochanter is made. The dissection is carried down and the fascia is incised in line with skin incision. The plane between the tensor fascia lata muscle anteriorly and the gluteus medius muscle posteriorly is bluntly developed using finger dissection (Figure 2). Blunt dissection is continued and the reflected head of the rectus femoris muscle is detached medially from the capsule. Retractors are inserted above and below the superior and inferior femoral neck. The capsule is then incised parallel to the neck extending from the inter-trochanteric line and up towards the acetabulum. Care should be taken to re-position the retractors deeper to the capsule to aid in the exposure and dissection. The capsulotomy is completed with clear exposure of the femoral head-neck junction and all of the femoral neck. Mild abduction, extension, and external rotation can facilitate exposure of the entire neck length.
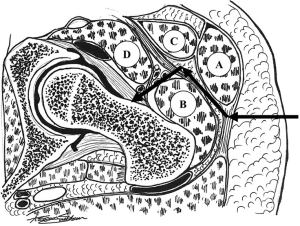
A preliminary cut is made in the femoral neck, at the femoral head-neck junction while aiming the oscillating saw distally to avoid inadvertent injury to the acetabulum. Traction is applied to the femur to open the osteotomy site and an elevator is used to deliver the femoral neck. The head is then removed from the acetabulum using a cork-screw or head spoon. While maintaining parallel position of the neck to the floor, a definitive cut is performed. Next, the leg can be placed back in neutral position and attention directed to the acetabulum which is reamed and the acetabular component placed. Then, the leg is dropped posteriorly behind the patient in a drape, in adduction, extension, and external rotation position, allowing the operating surgeon a clear access to the medullary canal. Reamers and rasps are and the femoral stem is placed. Following trials, the acetabular head with appropriate neck length is chosen and placed. The hip is then reduced and stability is checked. The capsular sleeves are approximated, the fascia is tightly repaired, and the subcutaneous tissue and skin is closed.
A standard post-operative protocol was instituted for all patients. This included immediate protected weight bearing from the day of surgery and physical therapy exercises under the supervision of an experienced orthopaedic physiotherapist. Weight-bearing protection was continued for the first post-operative week and gradually advanced over the second week. Occasionally, patients used wheeled walker for assistance for the first two weeks. All patients followed a standard post-operative thromboembolic prophylaxis regimen using subcutaneous low-molecular weight heparin and continue for 4 weeks post-operatively. Outpatient physical therapy was prescribed for every patient following discharge and continued for 4–6 weeks. Patients were evaluated by the operating surgeon at 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months intervals. For every patient, complications were reviewed according to the Hip Society standardized list of THA complications (23) and reported as frequencies. Additionally, OR times were collected by chart review for every patient. Subsequently, reported short-term complications and mean OR times in both cohorts were compared.
Literature review
A comprehensive literature search was conducted by searching the following databases; PubMed, EMBASE, EBSCO Host, and SCOPUS. Studies published between January 1st of 2000 and September 1st of 2017 were reviewed. The following key words were used in combination with Boolean operators “AND” or “OR” for the literature search; “Total hip arthroplasty”, “Röttinger”, “approach”, “direct lateral”, “lateral approaches”, “anterior approaches”, and “minimally-invasive”. We only included clinical studies that compared the Röttinger approach to other traditional approaches. Studies were excluded if they were single-cohort case series, case reports, cadaveric studies, and studies not in English language. The initial database search yielded 118 reports that were screened for relevant studies. This yielded 20 reports whose abstracts were thoroughly reviewed for eligibility according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Subsequently, 15 reports were excluded (10 case series, 3 were not in English language, and 2 case reports). Therefore, five studies were included in the final analysis. All studies were level III evidence.
Results
At mean follow-up time of 12 weeks (range, 6 to 24 weeks), there were two patients in the Röttinger cohort who experienced lateral femoral cutaneous nerve palsies (2%), which were self-limited and resolved at 6 and 12 weeks. In the direct lateral cohort, there was one hip dislocation (2%) at 6 weeks post-operatively, which was successfully managed by a closed reduction. No other complications were noted in both cohorts. Additionally, the mean operative times were comparable in both cohorts. In patients who received the Röttinger approach, mean OR time was 130 minutes (range, 74 to 202 minutes), compared to a mean of 111 minutes in the direct lateral cohort (range, 71 to 222 minutes).
In our literature analysis, five studies reported on 22,193 patients, comparing outcomes of the Röttinger approach in 2,252 patients to multiple other standard approaches in 19,941 patients (2,017 in anterior; 6,036 in posterior; and 11,888 patients in direct lateral) with follow-up range between 6 to 52 months. Findings demonstrated by these studies are detailed in Table 1. Patients in the Röttinger approach cohorts had less operative bleeding, smaller incisions, and slightly longer OR times. However, clinical outcomes and complications at minimum follow-up of 6 months did not differ significantly.
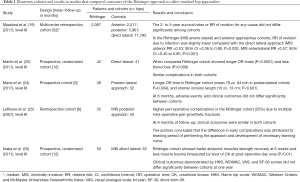
Full table
Discussion
Various surgical approaches have been developed and modified since Charnley first popularized THA (27). The goal of any approach is to provide adequate and safe access to the hip joint while minimizing soft tissue trauma. The Röttinger approach has recently gained interest among hip surgeons with its potential advantage of sparing the abductor muscles while allowing for adequate exposure with a relatively smaller incision (16,17). However, the success of any THA is dependent on a multitude of other variables beyond the surgical approach including patient selection, choice of implant, and performing soft tissue repair following implantation (3,28,29). Therefore, we specifically aimed to: (I) present our operative experience and technique of the Röttinger approach; (II) compare short-term complications and operative room (OR) times of this approach to the direct lateral; and (III) review the available comparative studies for primary THA. In this study, complications were comparable among cohorts. Moreover, the OR times were similar among patients who underwent surgery using this approach and those who received the direct lateral approach. Furthermore, the results of this study agree with our literature analysis of previous comparative reports which showed that patients who underwent primary THA using this approach had similar clinical outcomes and complications rate, along with less operative bleeding and comparable OR times. Therefore, we believe that with adequate experience, the Röttinger approach can be a safe alternative for primary THA.
This study is not without limitations. In this retrospective analysis, we only reviewed OR times and complications encountered over short-term follow up without accounting for other possible confounding factors. However, we aimed to investigate if a different approach can result in a markedly different perioperative and early post-operative outcome, which was not demonstrated in this study. Additionally, the relatively small total number of patients may undermine the power of the study and affect the generalizability of the results. However, all the surgeries were performed by the same surgeon which adds consistency to the observed clinical outcomes and complications.
Five studies have reported on the outcomes of the Röttinger approach in comparison to other THA approaches, all of which demonstrated no difference in clinical outcomes or complications between 6 to 52 months from the index surgery. The main findings that were statistically significant between cohorts were those demonstrated by Martin et al. (20) and Martz et al. (24) They showed that patients who were operated on using the Röttinger approach had less operative bleeding, smaller incisions and slightly longer OR times. Inaba et al. (26) showed that patients who underwent this approach had faster post-operative recovery of their abductor muscles. Additionally, they demonstrated a statistically significant lower level of muscle-creatinine kinase on post-operative day one, denoting less operative trauma. Laffosse et al. (22,25) emphasized on the role of surgeon experience to help avoid potential intraoperative complications as encountered in their cohort during earlier cases. In summary, the results of these studies have demonstrated that the Röttinger approach can be a safe alternative for use in primary THA.
To conclude, the development of hip approaches in THA continues to evolve with multiple modifications aiming to improve short and long-term clinical outcomes and to decrease the intraoperative morbidity. In this study, we presented our experience, illustrated the technique, and analyzed the current literature on the Röttinger approach in comparison to other standard hip approaches. Larger prospective, randomized, and comparative studies, are needed to further elucidate differences in outcomes for this approach vs. the others. However, our results as well as the current evidence, have demonstrated its safety and efficacy. With increased experience and exposure to this technique, it can be utilized as a routine hip arthroplasty approach.
Acknowledgements
None.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: Dr. Delanois is a consultant for, or has received institutional or research support from the following companies: Corin U.S.A, Orthofix Inc., Stryker. Dr. Mont is a consultant for, or has received institutional or research support from the following companies: Stryker, Cymedica, DJO Global, Johnson & Johnson, Microport, National Institutes of Health, Ongoing Care Solutions, Orthosensor, Pacira Pharmaceuticals, Peerwell, Performance Dynamics Inc., Sage, TissueGene. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The study was approved by the hospital’s institutional review board.
References
- Bremer AK, Kalberer F, Pfirrmann CW, et al. Soft-tissue changes in hip abductor muscles and tendons after total hip replacement: comparison between the direct anterior and the transgluteal approaches. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2011;93:886-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Arthursson AJ, Furnes O, Espehaug B, et al. Prosthesis survival after total hip arthroplasty--does surgical approach matter? Analysis of 19,304 Charnley and 6,002 Exeter primary total hip arthroplasties reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 2007;78:719-29. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Woo RY, Morrey BF. Dislocations after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1982;64:1295-306. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Masonis JL, Bourne RB. Surgical approach, abductor function, and total hip arthroplasty dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002.46-53. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Yang C, Zhu Q, Han Y, et al. Minimally-invasive total hip arthroplasty will improve early postoperative outcomes: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Ir J Med Sci 2010;179:285-90. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Matta JM, Shahrdar C, Ferguson T. Single-incision anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty on an orthopaedic table. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005.115-24. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Osborne RP. The approach to the hip-joint: A critical review and a suggested new route. Br J Surg 1930;18:49-52. [Crossref]
- Bauer R, Kerschbaumer F, Poisel S, et al. The transgluteal approach to the hip joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1979;95:47-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Hardinge K. The direct lateral approach to the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1982;64:17-9. [PubMed]
- Frndak PA, Mallory TH, Lombardi AV. Translateral surgical approach to the hip. The abductor muscle "split". Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993.135-41. [PubMed]
- Lin SJ, Huang TW, Lin PC, et al. A 10-year follow-up of two-incision and modified watson-jones total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Res Int 2017;2017:8915104. [PubMed]
- Mallory TH, Lombardi AV, Fada RA, et al. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty using the anterolateral abductor split approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999.166-72. [PubMed]
- Watson-Jones R. Fractures of the neck of the femur. Br J Surg 1936;23:787-808. [Crossref]
- DeWal H, Su E, DiCesare PE. Instability following total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2003;32:377-82. [PubMed]
- Iorio R, Healy WL, Warren PD, et al. Lateral trochanteric pain following primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2006;21:233-6. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Bertin KC, Röttinger H. Anterolateral mini-incision hip replacement surgery: a modified Watson-Jones approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004.248-55. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Hansen BJ, Hallows RK, Kelley SS. The Rottinger approach for total hip arthroplasty: technique and review of the literature. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2011;4:132-8. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Müller M, Tohtz S, Springer I, et al. Randomized controlled trial of abductor muscle damage in relation to the surgical approach for primary total hip replacement: minimally invasive anterolateral versus modified direct lateral approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2011;131:179-89. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Mjaaland KE, Svenningsen S, Fenstad AM, et al. Implant survival after minimally invasive anterior or anterolateral vs. conventional posterior or direct lateral approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2017;99:840-7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Martin R, Clayson PE, Troussel S, et al. Anterolateral minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2011;26:1362-72. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Laffosse JM, Accadbled F, Molinier F, et al. Anterolateral mini-invasive versus posterior mini-invasive approach for primary total hip replacement. Comparison of exposure and implant positioning. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008;128:363-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Laffosse JM, Chiron P, Accadbled F, et al. Learning curve for a modified Watson-Jones minimally invasive approach in primary total hip replacement: analysis of complications and early results versus the standard-incision posterior approach. Acta Orthop Belg 2006;72:693-701. [PubMed]
- Healy WL, Iorio R, Clair AJ, et al. Complications of total hip arthroplasty: standardized list, definitions, and stratification developed by the hip society. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2016;474:357-64. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Martz P, Bourredjem A, Laroche D, et al. Röttinger approach with dual-mobility cup to improve functional recovery in hip osteoarthritis patients: biomechanical and clinical follow-up. Int Orthop 2017;41:461-7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Laffosse JM, Chiron P, Molinier F, et al. Prospective and comparative study of the anterolateral mini-invasive approach versus minimally invasive posterior approach for primary total hip replacement. Early results. Int Orthop 2007;31:597-603. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Inaba Y, Kobayashi N, Yukizawa Y, et al. Little clinical advantage of modified Watson-Jones approach over modified mini-incision direct lateral approach in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2011;26:1117-22. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Charnley J. The long-term results of low-friction arthroplasty of the hip performed as a primary intervention. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1972;54:61-76. [PubMed]
- Howie DW, Holubowycz OT, Middleton R. Large femoral heads decrease the incidence of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2012;94:1095-102. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Pellicci PM, Bostrom M, Poss R. Posterior approach to total hip replacement using enhanced posterior soft tissue repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1998.224-8. [Crossref] [PubMed]


