Tricks to translating TB transcriptomics
Introduction
In 2013, an estimated 9.0 million people developed tuberculosis (TB) and 1.5 million died from the disease (1). Despite ongoing research efforts and ever-increasing knowledge of how Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) interferes with the human immune response, we are still far from developing the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches that would reduce the severity of this global epidemic. Vaccines form the cornerstone of potential eradication strategies of TB, yet the biological factors that provide protection from disease progression (so-called biological correlates of protection), which would assist design and testing of new vaccine candidates are lacking. A better understanding of natural protective immunity to TB would facilitate these attempts. Following inhalation of M.tb bacilli, latent TB infection (LTBI) is the most common outcome. It is considered that in LTBI the growth of the bacilli is contained by the coordinated host innate and adaptive immune response, preventing disease progression, but there is failure to completely eradicate all organisms, such that an underlying asymptomatic infection persists. This makes LTBI a particularly useful model system for the discovery of protective correlates.
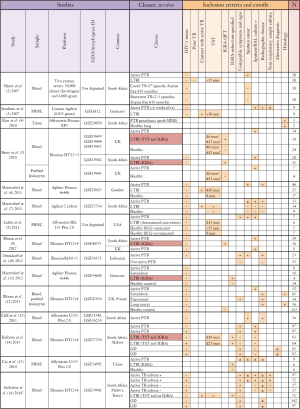
In the last 8 years, 15 transcriptomic studies have been published that use whole-genome gene expression microarrays in an effort to gain a broader understanding of the human response to M.tb infection, during various stages of pathogenesis and treatment (Figure 1). These studies have generally characterized the whole blood response, although the papers by Berry et al. and Bloom et al. (5,12) also investigated expression profiles on separated cell populations to delineate the effect of varying cell number and cell activation on the whole blood response. These studies provide evidence for correlates of risk of active TB, and have been remarkably concordant in their findings. In particular, they reveal an important role for type-I interferon signaling and neutrophil influx in disease pathogenesis, driving new areas of TB research. Moreover, they provide evidence that LTBI actually represents a spectrum of disease states: the whole blood signature of some LTBI cases clustered with those with active TB, suggesting these participants may be at risk of developing disease. The microarray data on which these studies are based have mostly been deposited in public databases (Figure 1), but generally the associated patient metadata is incomplete or unavailable. This significantly limits the utility of the data as the primary research can often not be reproduced. Without such detailed metadata, it can be challenging to meaningfully combine datasets in meta-analyses, even once the challenge of combining data from different platforms has been overcome. Moreover, while these studies provide evidence for blood biomarkers to diagnose active TB and monitor treatment, they have shed less light on correlates of protection against disease.
In a recent paper (17) published in Science Translational Medicine, Montoya et al. used an interesting combination of informatics and additional in vitro experiments to do just that. The novel strategy employed by the authors consisted of three components. Firstly, an idealized monocellular in vitro system was studied using transcriptomic approaches. The authors identified genes that correlate with defense response in differentiating macrophages, whose phenotype was previously associated with M.tb control (18,19). Hypotheses resulting from the first section were then tested in a second set of in vitro experiments. The final step involved further informatics analyses of existing human TB transcriptomic datasets to identify genes up-regulated in LTBI cases or which are decreased during active TB and increase during TB therapy. The three components were then integrated by determining the overlap of the genes sets from the in vitro and in vivo transcriptomic analyses in order to identify genes representing potential biomarkers of protective immunity. Via this method Montoya et al. identified IL-32 as a mediator of interferon gamma (IFNγ)-vitamin D mediated antimicrobial activity, and a marker of LTBI.
The importance of sample and patient characterization
While this novel approach yielded interesting candidate biomarkers of LTBI, there are a number of factors which must be taken into account to ensure this method yields translatable outcomes for understanding protective immunity (Table 1). Montoya et al.’s approach critically depends on how they differentiated and purified their in vitro cell populations, the differing proportions of circulating cell subsets between patient groups, and, critically, how they (or rather the authors of the original datasets) classified individuals as having LTBI.

Full table
Diagnosis of LTBI relies on the measurement of the adaptive response by tuberculin skin test (TST) or interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA), preformed on whole blood samples. Thus, these tests only inform us about immune memory, not current infection status; they cannot differentiate whether an individual eradicated the infection, either via the innate response or with help from the adaptive response. It has become clear that reliance on TST or IGRA-based classification approaches to define LTBI can result in very specific patient cohorts with different, and limited, disease phenotypes. Moreover, studies use different combinations of these tests to define LTBI (Figure 1). Thus better methods for defining LTBI are required; in particular, a marker for current M.tb infection, not based on immune sensitization. PET/CT imaging is one such approach that holds promise (20). When using LTBI as a model of protective immunity, it is therefore imperative that results are interpreted in the context of how patient groups were actually defined, particularly when an immune measure is used for classification; otherwise findings may be biased towards a specific phenotype. Moreover, outcomes need to be framed in the context of their derivation and not given a broad implication until validated on additional patient cohorts.
The cellular composition of samples from which RNA was extracted for these analyses is the second vital component to interpreting the results from transcriptomic studies. Whole-blood signatures are highly influenced by differing proportions of circulating cell populations, which obviously differ by disease states. Many of the differences in T cell transcripts identified between individuals with TB and healthy controls, identified by Berry et al. (5), were ascribed to decreased circulating lymphocyte numbers in TB patients, rather than functional differences in cells. TB is known to be a disease of relative lymphopenia and neutrophilia, thus, it may be predictable that whole-blood from TB patients is dominated by a neutrophil-driven transcriptomic response. Moreover, extrapolating observations in blood to processes of disease pathogenesis occurring at the site of disease remain problematic. Although this comparison does identify biomarkers of TB disease, in comparison to someone who is healthy, what is actually required is a disease-specific signature. Thus, a more rigorous comparison should include a third group of individuals with similar symptoms but differing etiology. Three such studies have performed this (Figure 1), two comparing TB and sarcoidosis patients (11,12), another granulomatous lung disease, and one comparing TB patients and respiratory symptomatics with other diagnoses (14). In their study, Bloom et al. found the signature of TB and sarcoidosis to cluster together, when compared to pneumonia and lung cancer, and both to be dominated by interferon-inducible transcripts. Thus, one must be extremely careful when conducting any transcriptomic study to ensure the interpretation of the differentially expressed genes are contextualized with regard to the disease states of the individuals, the effect of the disease state on the peripheral blood compartment and how it may relate to processes at the site of disease.
Finally, not only is it vital to acknowledge the effect of differing proportions of cell types in differing disease states, during a whole-blood comparison, but also the purity of an isolated cell population from in vitro or ex vivo analyses, when results are to be extrapolated to a particular cell type. Montoya et al. made particular note of this latter point, in relation to describing unexpected gene expression results from purified CD14+ monocyte cultures to the presence of potentially contaminating CD8 T cells. There must be consistency in how results are interpreted. If unexpected results are attributed to an unknown percentage of contaminating cells it can become difficult to ascribe other observations from the same data solely to the predominant cell population.
The paper by Montoya et al. is novel in its approach and is rich in data. But, to interpret the relevance of their findings, it is necessary to carefully examine the methods, both in vitro and the complex informatics that form the backbone of the authors’ findings. Immunologically, the in vitro methods are logical and easy to follow; based on their previous finding that IL-15 differentiates monocytes into macrophages exhibiting an M1-like phenotype with antimycobacterial properties (18,19), they extracted RNA for microarrays (GEO accession GSE59184) from CD14+ selected monocytes (90% purity) derived from adherent peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors treated for 6 and 24 hours with IL-15, IL-4 and IL-10 (to generate M2-like macrophages) or media control. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was then applied to the data and forms the crux of understanding all informatics analyses conducted in this study. This systems biology approach has the potential to elucidate novel pathways of cellular interaction which is vital to our understanding the complex disease pathogenesis of TB; but to correctly interpret its output, an understanding of the methodology is required.
Translating modular analyses
The WGCNA algorithm identifies modules of co-expressed genes whose transcript abundance co-varies across samples by correlation and clustering analysis. For each module, a module eigengene (ME) is determined; this represents the first principal component of the expression data matrix for the module (a genes × b samples). This ME summarizes the expression of the module in a single number, it does not represent one gene in the module, but all genes. Then the matrix of module eigengenes (m modules × by b samples) and the matrix of phenotype variables (b samples × p phenotypes) are correlated with a resulting m × p correlation matrix. This matrix provides information on the association between modules and phenotype. In the Montoya et al. paper, only a single module (MEblack) is highlighted as biologically relevant, being the most positively correlated with IL-15 treatment; all other modules are excluded in further discussion. The black module is enriched for the gene ontology (GO) term “defense response” (48 genes out of 802 probes), and contains IL32. Next, 36 “myeloid defense genes” are defined, characterized as any of these 48 defense response genes expressed in resting myeloid cells, as determined from a preexisting transcriptional dataset (21). Interestingly the authors define IL32 as myeloid-derived despite lymphoid cells being the predominant cells expressing it in their comparison of 24 gene-sets from resting cells. They further support the myeloid origin of IL32 by reference to studies identifying its expression by monocytic cells following IFNγ, TLR4 or NOD2 activation; an alternate interpretation of this data is that IL32 expression is induced by stimulation and not abundant in resting myeloid cells. Other “defense-response” genes were labeled myeloid-derived based on their informatics approach alone and it highlights the need for consistency in the interpretation and selection of candidate genes which become the focus of further analyses. The top interactions for these myeloid-defense genes were then visualized using the network visualization and analysis tool VisANT and consequently IL32 was linked to the vitamin D antimicrobial pathway, via correlation with CYP27B1 induction, which encodes the final enzyme needed to activate vitamin D.
Avoiding selective bias
While the authors elegantly demonstrate with subsequent in vitro silencing experiments that IL-32, reliant on vitamin D, is a downstream gene in the IFNγ antimicrobial pathway, it would have been of interest to have more information about the module in which IL32 was identified, including the gene list for IL15black, the fold-change of IL32, direction of induction of and its position in the list of genes regulated by IL-15. It is clear IL32 is an important gene in this module, but there are others, which may also pose as potential correlates of protection. This is a fundamental issue researchers working with transcriptomic data now face; given a list of 100 interesting genes, what is the basis for further investigation? Supervised selection of genes may bias outcome and more high-throughput methods for robust validation and confirmation using in vivo systems is required. When researchers are selective, they must ensure their approach is transparent and reproducible. They must provide all gene lists which guided their selective approach, to ensure their outcomes are not biased and their findings are placed within the context of the greater gene regulation network(s).
The final section of the paper focuses on mining existing transcriptomic datasets from patients with active TB, LTBI or healthy controls, utilizing four of the 15 available studies (5,9,11,14). The overall approach is to identify genes that are more highly expressed in individuals with LTBI (diagnosed using a combination of TST, Quantiferon Gold and in-house IGRA assays) compared to those with either active TB or healthy controls (asymptomatic IGRA-negative). One of these studies (9) also investigated the transcriptional response during TB treatment, and was used to identify genes highly expressed in LTBI, which are low at TB diagnosis and increase during treatment. The previously identified IL15black module from the macrophage microarray experiments was then overlapped with the LTBI-high genes and with the one module from the response to treatment analysis, which was selected on the basis that it contains IL-32. Four other modules from the TB treatment data set actually show a more significant ME for genes which increase during treatment, but these do not contain IL-32 and are therefore not followed-up. Thus there remain many uninvestigated but interesting modules, which may provide further potential correlates of protection, but which were deprioritized in a somewhat self-fulfilling approach.
While it is clear that IL32 has a role in antimicrobial immunity, there are two methodological issues which may arise in any TB OMICS study, which should heed caution to it being defined an a correlate of protective immunity, until further validation. Firstly, the immunological basis of LTBI diagnosis, secondly, the differences in cell populations between healthy and disease individuals. As the LTBI group used in this study was defined by IGRA positivity, and thus their greater ability to produce IFNγ, it is potentially self-fulfilling that transcripts associated with the IFN-γ pathway, i.e., IL32, were identified to be more abundant in latent vs. healthy individuals. Moreover, IL32, which is predominantly expressed by lymphoid cells, is less abundant in active TB, a state of peripheral lymphopenia, and the increase in IL32 during therapy is coincident with peripheral lymphocyte reconstitution. Thus, the lack of the marker in TB may merely be a reflection of the peripheral blood state of disease and not necessarily a functional defect resulting in loss of protective immunity. These issues highlight the importance of using non-immunological criteria for patient group classification and the need to adjust for differences in the cellular composition of samples compared between groups.
The future of TB OMICS
Translational Medicine increasingly relies on high-throughput data to inform hypothesis generation and system descriptions. While the generation of such data is becoming routine; increasingly complex informatics approaches are being utilized in order to optimally extract information from the data. Based on our interpretation, it is not clear that the approach used to identify correlates of protection from active TB was truly unsupervised, but rather semi-supervised and it appears that the study conclusions were to some extent self-fulfilling. Despite these limitations, such systems approaches to identify correlates of protection using existing data sets are useful, as is the use of transcriptomics to identify novel pathways of protection from in vitro cultures. For the informatics approaches to work best, higher-quality patient-level metadata is required for published transcriptomic datasets. Such information is crucial to account for differences in populations, disease presentation, M.tb exposure and underlying co-existent conditions (infections and non-communicable diseases). Ownership of such data and authorship of future manuscripts using this data may become complex. However, if we are to move towards utilizing the wealth of data accumulated over the last decade, in order to provide the crucial insights needed to advance TB research, this is a step researchers need to tackle.
To fully utilize the information from high-throughput OMICS approaches, there is the need to develop a platform for data integration. This should systematically capture all information from transcriptomics, proteomics and detailed clinical phenotype data. There should be an emphasis on shared relationships and common associations in order to develop a multiscale model of the biology of the host response to TB, constrained by unbiased, high-throughput observations. We therefore propose the time is ripe for the field of TB-OMICS to convene a combined workshop for all groups who have deposited large OMICS data sets to define how to proceed to look for translational outcomes for these data, specifically markers of protection, diagnostics and treatment monitoring.
Acknowledgements
Funding: A Deffur acknowledges funding from the Hasso Plattner Foundation. RJ Wilkinson acknowledges the following funding sources: Wellcome Trust (UK): 084323, 104803; MRC (UK): U1175.02.002.00014; FP7-HEALTH-F3-2013-305578; MRC-SHIP-02-2013. AK Coussens acknowledges funding from Academy of Science of South Africa and MRC-SHIP-02-2013.
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. Available online: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/
- Mistry R, Cliff JM, Clayton CL, et al. Gene-expression patterns in whole blood identify subjects at risk for recurrent tuberculosis. J Infect Dis 2007;195:357-65. [PubMed]
- Jacobsen M, Repsilber D, Gutschmidt A, et al. Candidate biomarkers for discrimination between infection and disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007;85:613-21. [PubMed]
- Kim MJ, Wainwright HC, Locketz M, et al. Caseation of human tuberculosis granulomas correlates with elevated host lipid metabolism. EMBO Mol Med 2010;2:258-74. [PubMed]
- Berry MP, Graham CM, McNab FW, et al. An interferon-inducible neutrophil-driven blood transcriptional signature in human tuberculosis. Nature 2010;466:973-7. [PubMed]
- Maertzdorf J, Ota M, Repsilber D, et al. Functional correlations of pathogenesis-driven gene expression signatures in tuberculosis. PLoS One 2011;6:e26938. [PubMed]
- Maertzdorf J, Repsilber D, Parida SK, et al. Human gene expression profiles of susceptibility and resistance in tuberculosis. Genes Immun 2011;12:15-22. [PubMed]
- Lesho E, Forestiero FJ, Hirata MH, et al. Transcriptional responses of host peripheral blood cells to tuberculosis infection. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2011;91:390-9. [PubMed]
- Bloom CI, Graham CM, Berry MP, et al. Detectable changes in the blood transcriptome are present after two weeks of antituberculosis therapy. PLoS One 2012;7:e46191. [PubMed]
- Ottenhoff TH, Dass RH, Yang N, et al. Genome-wide expression profiling identifies type 1 interferon response pathways in active tuberculosis. PLoS One 2012;7:e45839. [PubMed]
- Maertzdorf J, Weiner J 3rd, Mollenkopf HJ, et al. Common patterns and disease-related signatures in tuberculosis and sarcoidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:7853-8. [PubMed]
- Bloom CI, Graham CM, Berry MP, et al. Transcriptional blood signatures distinguish pulmonary tuberculosis, pulmonary sarcoidosis, pneumonias and lung cancers. PLoS One 2013;8:e70630. [PubMed]
- Cliff JM, Lee JS, Constantinou N, et al. Distinct phases of blood gene expression pattern through tuberculosis treatment reflect modulation of the humoral immune response. J Infect Dis 2013;207:18-29. [PubMed]
- Kaforou M, Wright VJ, Oni T, et al. Detection of tuberculosis in HIV-infected and -uninfected African adults using whole blood RNA expression signatures: a case-control study. PLoS Med 2013;10:e1001538. [PubMed]
- Cai Y, Yang Q, Tang Y, et al. Increased complement C1q level marks active disease in human tuberculosis. PLoS One 2014;9:e92340. [PubMed]
- Anderson ST, Kaforou M, Brent AJ, et al. Diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis and host RNA expression in Africa. N Engl J Med 2014;370:1712-23. [PubMed]
- Montoya D, Inkeles MS, Liu PT, et al. IL-32 is a molecular marker of a host defense network in human tuberculosis. Sci Transl Med 2014;6:250ra114.
- Krutzik SR, Hewison M, Liu PT, et al. IL-15 links TLR2/1-induced macrophage differentiation to the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway. J Immunol 2008;181:7115-20. [PubMed]
- Fabri M, Stenger S, Shin DM, et al. Vitamin D is required for IFN-gamma-mediated antimicrobial activity of human macrophages. Sci Transl Med 2011;3:104ra102.
- Ghesani N, Patrawalla A, Lardizabal A, et al. Increased cellular activity in thoracic lymph nodes in early human latent tuberculosis infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014;189:748-50. [PubMed]
- Swindell WR, Johnston A, Voorhees JJ, et al. Dissecting the psoriasis transcriptome: inflammatory- and cytokine-driven gene expression in lesions from 163 patients. BMC Genomics 2013;14:527. [PubMed]


